Since the completion of the main stage of the legendary mission “Rosetta” took several months. Over the short term lander “Fila” on the surface of the nucleus of comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, scientists have gathered enough information to get answers to their questions.
Now, researchers published the first scientific article with detailed results of the analysis of data from the instruments apparatus “Rosetta” and lander “Fila”. It is already clear that this mission has made the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko comet most studied in the history of mankind.
The first scientific article, like all the others, published in the journal Science. It describes the comet in terms of density and weight loss among its parts. For the analysis of planetary scientists used data from the optical, spectroscopic and infrared remote sensing system OSIRIS.
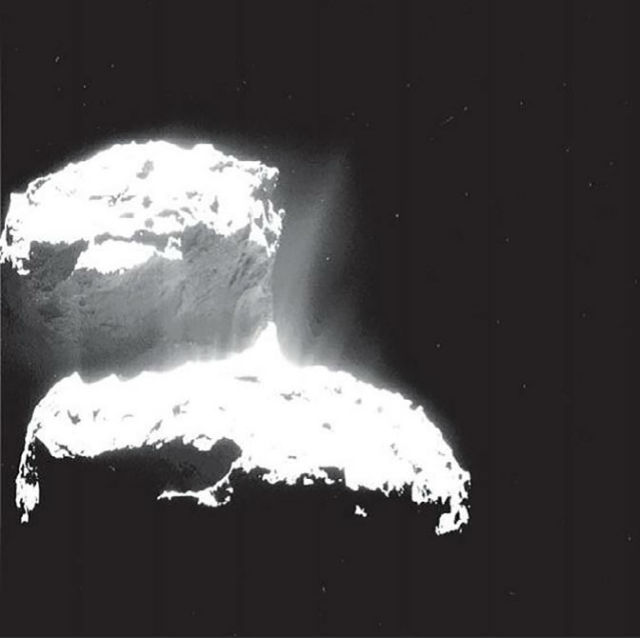
Comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, recall, is shaped like a child’s rubber duck. It was found that the gravitational pull of 67P maximum at the top of the core and about six times weaker than in the “neck” of the comet. This is indicated by the fact that the dust from the comet’s nucleus in its “neck” rises much more frequently than in other regions it.
get an accurate shape of the comet once again raises the question of whether the Churyumov -Gerasimenko result of a collision of two bodies 4.5 billion years ago or it was originally a single entity, but over time due to the gradual loss of mass formed division. If true would be the second hypothesis, it will be necessary to answer the question of why such a powerful erosion in the “neck” of the comet.

In order to determine which of the two versions is correct, it will be necessary to compare the structure of the two parts of the comet – “trunk” and “the head”. If they are similar, it is likely, Churyumov-Gerasimenko has always been one celestial body, and if they differ, it is likely that this comet – the result of the coalescence of two bodies.
Meanwhile, a team of scientists used data collected to calculate the density of the comet and determined that a celestial body is very porous. Moreover, the core 67P has a density less than half than that of water, and the potential to drift on the surface of the world’s ocean.
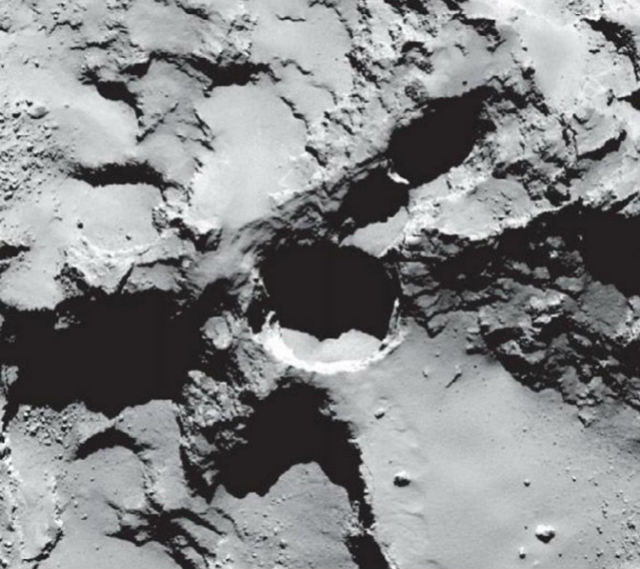
The images taken with the camera OSIRIS, also helped to identify the various features of the comet planetologicheskie (picture resolution was about 0.8 meter per pixel). About detected on its surface dunes, ridges and canyons of the researchers told the second scientific article.
Planetary conditionally divided the surface of a comet into several regions depending on the structure of the surface of a celestial body. Each region was named after the ancient Egyptian gods. For example, in honor of the goddess-called fish Hatmehit smooth depression on the “head” utkoobraznoy comet. This basin is similar in its morphological features on cosmic dust-filled impact crater.
The rocky regions of the comet’s nucleus were named in honor of the god of chaos and Seth sandstorms and the goddess of love, femininity and beauty Hathor. However, the sheer cliffs Churyumov-Gerasimenko for little resemblance to the earth: analysis indicates that this is just compacted dust. The study also showed that many of the structures formed by circulation of gas and dust near the surface, just like the wind shapes the sand dunes in the Earth’s deserts.
According to the authors of one study, detailed images with a resolution, reaching up to 15 centimeters per pixel, show structure, which can be restored early history comet. So, for example, the images of the region Seth were found three-meter hills, was nicknamed “creepy.” Later, scientists discovered them over the entire surface of the comet.
Zirks Holger (Holger Sierks), principal investigator and OSIRIS camera Fellow of the Institute for Solar System Max Planck Society, said that the “goose bumps” could be formed at the dawn of the solar system itself from the grains of dust and ice, stuck together under the influence of various forces.
“We assume that Similar structures can be all comets of our planetary system, and the grains of dust and ice constitute the building blocks of these celestial bodies “, – says Zirks.
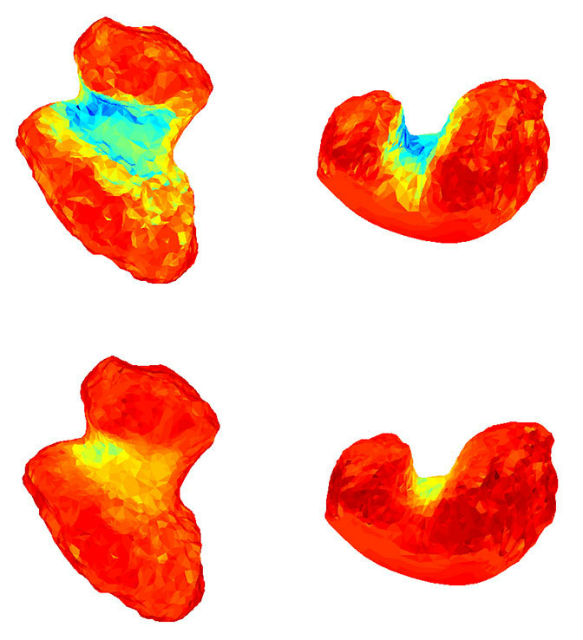
These multiple tools show that the” neck “of the comet is the source of most it flows of gas and dust. To understand why this area is so active, the “Rosetta” conducted simulation. Scientists have determined the amount of thermal energy falling on the surface of a comet for the 12.4-hour rotation around its axis and 6.5-year orbit around the sun.
As it turned out, “neck” of the comet gets less energy from the sun than the rest of its area, as always in the shade. However, as it turned out, that in this region there is a so-called effect geliopriёmnika – accumulation of solar energy – due to the fact that the radiation is reflected from the cliffs on both sides of the cleft. Because of this condition compensated eternal shadows.
Other possible reasons for the high activity of the region can be to its low gravity. This means that the formation of dust storms need less power than in other regions, and hence the structure planetologicheskaya “neck” may be different from all other regions of the comet. Moreover, the researchers conclude that in this area the water can be closer to the surface.
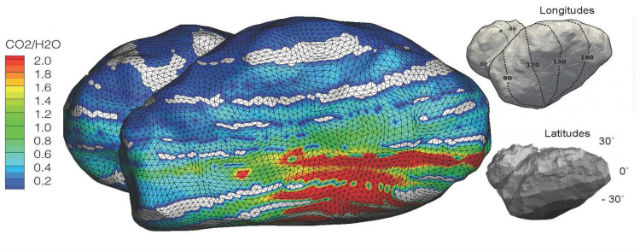
As part of another study, the results of which is told in the third scientific article, scientists studied the composition of the towering structures on the surface of a comet. Monitoring with orbital spectrometer ROSINA demonstrated different levels of water in the comet, oxide and carbon dioxide.
On the basis of the data the researchers mapped, which pointed to the fluctuations in the ratio of carbon dioxide to water, observed over the entire surface with August 17 to September 22, 2014. The composition, according to scientists, is changing with the 12.4-hour rotation period of the comet around its axis, as well as the change of seasons.
The fourth study was to analyze the optical and infrared portraits Churyumov-Gerasimenko surface made spectrometer VIRTIS. Pictures show the abundance of opaque organic compounds and an extremely small amount of water ice, which is contrary to all previous expectations of scientists.

The analysis of these images indicates that the comet formed in the Kuiper Belt, located beyond the orbit of Neptune. Interestingly, the study of the trajectory of the Churyumov-Gerasimenko, the solar system showed that the comet was formed closer to Jupiter. However, new data refute this version.
Another team of scientists compared the data OSIRIS camera and another vehicle tool – dust analyzer GIADA. This work was aimed at studying the coma, dense clouds of dust and gas that surrounds the comet nucleus. As we approach the comet to the Sun, coma becomes more massive as the core heats up and gives more dust and gas into space.
By measuring the activity in a coma, including changes in the ratio of dust and gas, scientists sought to evaluate how quickly Churyumov-Gerasimenko is losing its weight and how fast it is the process of decontamination. How to tell the scientists in the final article, the surface of the comet was discovered cloud of particles orbiting the comet, but with sufficient mass to fall onto its surface. This is contrary to conventional ideas about the gravitational field of a celestial body.
Another article describes the efforts of the team of scientists involved in the study of the magnetosphere of a comet. How to tell the planetary, solar wind penetrates the thin atmosphere of the comet (created sublimated from the surface substances). But the pressure of the ionized gas in the atmosphere changes as it approaches the surface, because of which formed more or less clear boundaries, for which the particles emanating from the sun can not get through. Thus was born the magnetosphere of a celestial body.
The team used data analyzer ion composition IRF, to detect the ions of water in the outer layers and closer to the surface 67P. It turned out that Churyumov-Gerasimenko atmosphere begins to repel the solar wind from a distance about 3.3 astronomical units.
The study also showed that the water at the surface of the comet contains accelerated high-energy ions, as well as locally formed low-energy ions. Evaluation of both streams of particles allows us to understand the essence of the magnetosphere of a celestial body.
The last of the published articles describes the properties of the subsurface structure of the comet. With microwave detector MIRO scientists have determined that the total loss of water Churyumov-Gerasimenko in range from 0.3 kilograms per second, according to the beginning of June 2014, to 1.2 kilograms per second, at the end of August 2014. This indicates that the periodic fluctuations in the number of outgoing H 2 O associated with the rotation of the nucleus and its form.
In the future, scientists will publish more number of scientific articles with results of analyzes of the data collected during the mission “Rosetta”. It is likely that much of the information received, it will be necessary to double-check by other devices.
No comments:
Post a Comment