Riddle disappeared oceans of Mars: the giant tsunamis up to 120 m washed away coastal areas for hundreds of kilometers inland
The study, published in Scientific Reports , hypothesizes that explains the absence of traces of ancient Martian oceans. Scientists believe that the asteroid impact led to the formation of giant waves that washed the shores of the seas of Mars. That is why traces of these shores is still not detected, although there is plenty of evidence of the existence of large amounts of liquid water on ancient Mars.
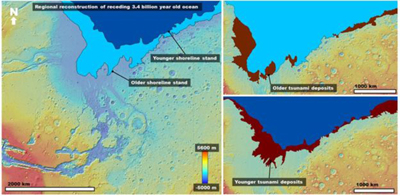
The most powerful tsunami swept on Mars for hundreds of kilometers inland
Researchers have long speculated that the depressions in the northern hemisphere of Mars about 3.4 billion years ago, experienced the incredible scale flooding that formed a vast ocean area in millions of square kilometers. However, this hypothesis was not enough evidence of the main: the coastline. Its traces are still not found in those regions where the need to preserve the traces of the coast once a large and deep ocean.
With the help of cameras spacecraft Mars Odyssey Orbiter, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and Mars Global Surveyor scientists have studied the alleged former Ocean region on the border of the mountain and lowland areas. The researchers carefully examined ancient rocks and terrain, especially placers of boulders and water ice.
According to the scientists, these deposits are the next two most powerful tsunami that swept across the Martian landscape and wiped out the ancient ocean coast line. Computer models have shown that the cause of the tsunami could be hitting big asteroid with an average height of about 50 m, and the most powerful tsunami had a wave height of more than 120 m. The huge mass of water crumbled rocks in the gravel, washed the shore and washed away the top layer of the soil for hundreds of kilometers inland the coastline.
Most likely cause of the tsunami was the fall of large asteroids that formed impact craters with a diameter of 30 km. At the same time similar disaster occurred with all the oceans of Mars about once every 3 million years. Simply put, scientists have found traces of the tsunami only two, but certainly there were more.
Thus, today we see the tragedy of ancient Mars, which had all the conditions for life and development of the biosphere. Such a planet would be a boon to mankind, but merciless cosmic catastrophe literally torn to pieces by Mars, leaving him a chance.
No comments:
Post a Comment