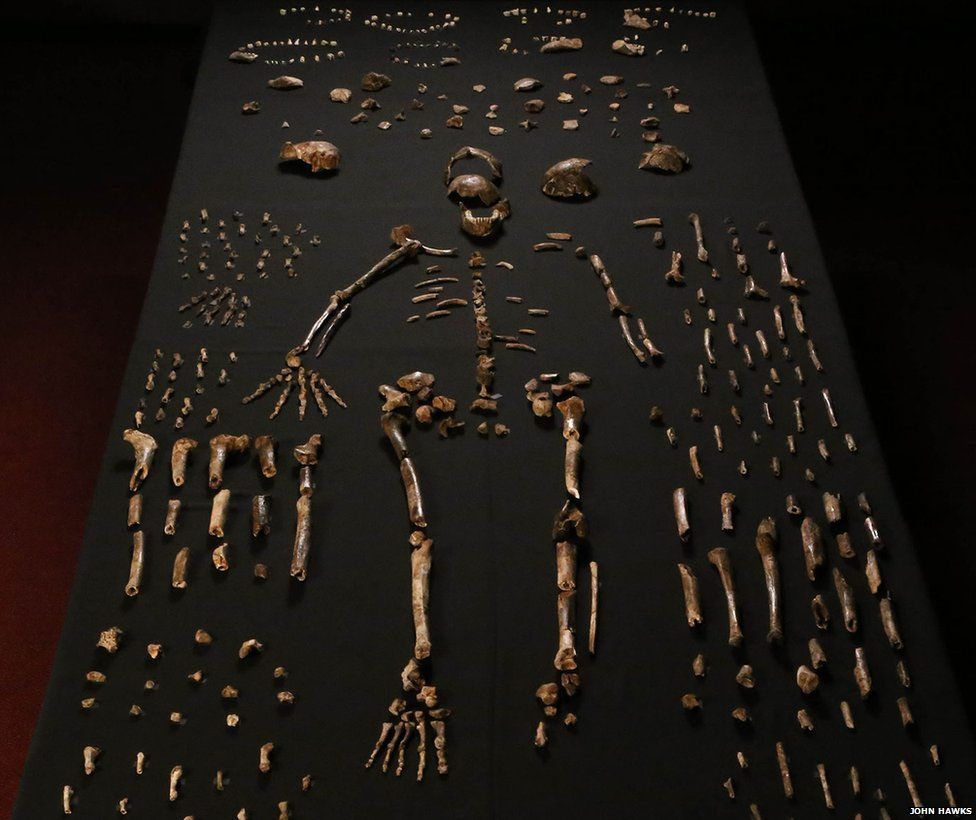
In southern Africa, found the remains of 15 partly preserved skeleton related to the modern human species that lived on our planet about 3 million years ago.
In an article published in the journal Elife, it emphasized that this finding dramatically changes the perception of the ancient progenitors of man is one of the most important in recent times.
Professor Lee Berger, who led the expedition, in an interview with BBC BBC said that nothing like this had never seen or even imagined that such a discovery is possible at all. He also said that, in his opinion, these creatures were among the first in the chain leading to modern man.
“found the first bone, we were hoping to find at least the remains of a creature, and as a result have found several skeletons. By the end of the three-week expedition found out that found the biggest burial of the remains of relatives of a person in the history of Africa “- said Professor.
Who is he – Homo naledi?
15 skeletons, the bones of which are perfectly preserved, were found in one of the underground caverns.
Representatives of the new species are called Homo naledi . Scientists have carried them to the genus Homo, to which modern man, and believe that these creatures had the ability to a certain ritual behavior.
Professor Lee Berger, he said that would not be in this case, to use the term “missing link” (from ape to man), but nevertheless believes that this species was a kind of bridge from primitive bipedal primates to humans.
Professor Chris Stringer said that the discovery of naledi – it is extremely important for science discovery.
“All the finds of recent years suggests that in different parts of Africa, the nature of experimenting, developing several different types of humanoid creatures. But only one of these lines was able to survive,” – says the scientist in an interview with BBC BBC.
Professor Lee Berger said that the previous understanding of the ancient species of man based only found individual bones and the skull of humanoids.
Tunnel to the ancestors
Now the skeletons naledi , found in Africa, are at Witwatersrand University. All are neatly from the youngest to the more mature.
Professor Berger said that shocked at how well preserved remains – bones, skull, teeth.
“This finding may to help us figure out all the details of the lives of these creatures when they were born, how long the mother fed them with her milk, as they developed, how fast passed their development as different lifestyle males from women as they grow old and die, “- he says scientist.
Homo naledi is very different from all previous finds of this kind. They are, judging by the remains, they had a small brain size is comparable to the size of a gorilla brain, and the structure of the pelvic and shoulder bones were very primitive. But scientists still carried those creatures in the genus of people due to the development of the skull, the relatively small size of the teeth and the longer legs and the structure of the foot.
The cave where the skeletons were found, it lies in the valley, known as the “Cradle of Humankind”. It leads to a narrow cramped tunnel that can only crawl to get into the cave itself. The way it takes about 20 minutes.
Scientists believe that the cave was used naledi for the burial of the dead, and they made this ritual for generations. If this is confirmed, it will be proof that early humans mastered the ritual is not 200 million years ago as previously thought, but much earlier.
Further details of the lives of these creatures, according to scientists, can change our the idea evolved as a person and as a complex and rich history of mankind was.
No comments:
Post a Comment